Forces and Impulses
Use the cursor keys to apply impulses, the WASD keys to apply torques and rotate the cube. Press and hold F to apply a constant upward force to cancel gravity effects. Press R to reset the cube.
Try to get the cube to balance and spin on one of its corners! The full code used is shown at the bottom of this page.
In this tutorial we will show you how to use forces to control a dynamic rigidbody and produce the demo shown above. We will briefly show the use of forces, impulses, torques and the use of rigidbody component UI to customize behavior.
Scripting Forces
Applying a Constant Force
if (app.keyboard.isPressed(pc.KEY_F) ) {
this.entity.rigidbody.applyForce(0, 9.8, 0);
}
Here a force along the global y-axis is applied to the accessed entity when the user presses the F key via applyForce(x, y, z). The point of application of the force vector can
also be set.
Impulses
if (app.keyboard.isPressed(pc.KEY_LEFT) ) {
this.entity.rigidbody.applyImpulse(-1, 0, 0);
}
The cube is given an x-axis impulse to impart an instant change of velocity via applyImpulse(x, y, z).
Torques
if (app.keyboard.isPressed(pc.KEY_W) ) {
this.entity.rigidbody.applyTorque(-this.torque, 0, 0);
}
Torques (rotational forces) are applied to the entity via applyTorque(x, y, z).
TorqueImpulses
this.entity.rigidbody.applyTorqueImpulse(x, y, z)
Instantaneous changes in angular velocity are applied via applyTorqueImpulse(x, y, z). This was not used in the code for
the above demo.
Moving dynamic rigidbodies
In order to move rigidbodies, you apply linear forces and rotational forces (torque) using the methods above. Usually you should try to avoid directly modifying the position or velocity of a rigidbody as this will override the simulation and it can lead to odd effects, especially when objects collide.
However, if you need to, you can override the velocity by assigning a new 'pc.Vec3' set of values
directly to entity.rigidbody.linearVelocity or entity.rigidbody.angularVelocity.
For more information on rigidbody types, see the collision API page, the pc namespace page, the fps-controller tutorial and the collision tutorial.
General setup
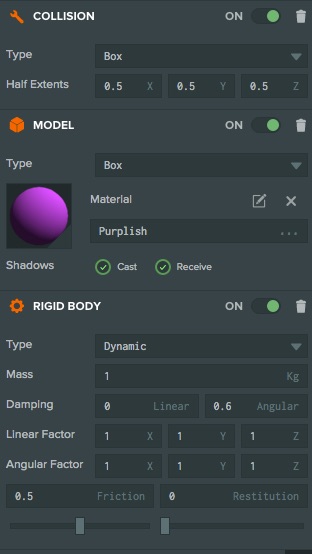
We set up a basic scene with a spotlight, a cube (entity with model, rigidbody, collision and script components) and a floor (with model, rigidbody and collision components). The cube's rigidbody was set to dynamic while the floor's rigidbody was set to static. We created some materials for each box and changed the diffuse colors just to make it easier on the eye. We have also activated the 'cast shadows' option on both the SpotLight and DynamicBody entities. The full 'usingForces' Scene and code for this PlayCanvas app can be found here.
Limiting and control
Some Editor settings were set to prevent the constant application of unbalanced forces (and so prevent a body from continuously accelerating and moving out of control). We enabled angular damping on the cube's attribute editor as well as friction on both the cube and floor. Linear damping is not used here, however it can be used to simulate air resistance, and of course decelerations can be applied as required via code.
Teleporting a Body
To instantly teleport a body to a new position, you can't use the setPosition function from the pc.Entity API. This is because the physics engine would still think the body is in the old location. Instead, you have to use the rigidbody component's teleport function:
//code within the update function
this.playerPos = this.entity.getLocalPosition();
// Keeping the cube on screen - cube moves off of one screen edge then appears from the opposite edge.
if (this.playerPos.x < -9.0) {
this.entity.rigidbody.teleport(8.8, this.playerPos.y, this.playerPos.z);
}
if (this.playerPos.x > 9.0) {
this.entity.rigidbody.teleport(-8.8, this.playerPos.y, this.playerPos.z);
}
If the cube moves beyond the viewable area in the x-direction, the teleport function is called and the cube entity is teleported across the
screen. The entity is teleported to a less extreme left/right position so as not to continuously activate the if() statement.
Reset cube code
if (app.keyboard.wasPressed(pc.KEY_R)) {
this.reset();
}
reset: function () {
this.entity.rigidbody.teleport(0, 2, 0);
this.entity.rigidbody.linearVelocity = pc.Vec3.ZERO;
this.entity.rigidbody.angularVelocity = pc.Vec3.ZERO;
}
We include a reset function that brings the cube to its original position and, as mentioned above, synchronizes the rigidbody's location to that of the teleported entity. The final two lines in the reset function reset the body's linear and angular velocities to zero. The object's orientation could also be reset, but is not carried out in this code.
Full code listing
var DynamicBody = pc.createScript('dynamicBody');
// initialize code called once per entity
DynamicBody.prototype.initialize = function() {
this.torque = 7;
this.app.keyboard.on(pc.EVENT_KEYDOWN, this.onKeyDown, this);
this.on('destroy', function() {
this.app.keyboard.off(pc.EVENT_KEYDOWN, this.onKeyDown, this);
}, this);
};
DynamicBody.prototype.onKeyDown = function (event) {
event.event.preventDefault();
};
// update code called every frame
DynamicBody.prototype.update = function(dt) {
//update player's position
this.playerPos = this.entity.getLocalPosition();
var app = this.app;
//keyboard controls and applying forces and moments.
if (app.keyboard.isPressed(pc.KEY_LEFT) ) {
this.entity.rigidbody.applyImpulse(-1, 0, 0);
}
if (app.keyboard.isPressed(pc.KEY_RIGHT) ) {
this.entity.rigidbody.applyImpulse(1, 0, 0);
}
if (app.keyboard.isPressed(pc.KEY_UP) ) {
this.entity.rigidbody.applyImpulse(0, 1, 0);
}
if (app.keyboard.isPressed(pc.KEY_A) ) {
this.entity.rigidbody.applyTorque(0, this.torque, 0);
}
if (app.keyboard.isPressed(pc.KEY_D) ) {
this.entity.rigidbody.applyTorque(0, -this.torque, 0);
}
if (app.keyboard.isPressed(pc.KEY_W) ) {
this.entity.rigidbody.applyTorque(-this.torque, 0, 0);
}
if (app.keyboard.isPressed(pc.KEY_S) ) {
this.entity.rigidbody.applyTorque(this.torque, 0, 0);
}
if (app.keyboard.isPressed(pc.KEY_F) ) {
this.entity.rigidbody.applyForce(0, 9.8, 0);
}
// Keeping the cube on screen - cube moves off of one screen edge then appears from the opposite edge.
if (this.playerPos.x < -9.0) {
this.entity.rigidbody.teleport(8.8, this.playerPos.y, this.playerPos.z);
}
if (this.playerPos.x > 9.0) {
this.entity.rigidbody.teleport(-8.8, this.playerPos.y, this.playerPos.z);
}
// cube reset control
if (app.keyboard.wasPressed(pc.KEY_R) ) {
this.reset();
}
};
DynamicBody.prototype.reset = function () {
this.entity.rigidbody.teleport(0, 2, 0);
this.entity.rigidbody.linearVelocity = pc.Vec3.ZERO;
this.entity.rigidbody.angularVelocity = pc.Vec3.ZERO;
};